Value added tax
 |
|
Policies
Government revenue
Tax revenue · Non-tax revenue Law · Tax bracket Exemption · Credit · Deduction Tax shift · Tax cut · Tax holiday Tax advantage · Tax incentive Tax reform · Tax harmonization Tax competition · Double taxation Tax, tariff and trade |
|
Price effect · Excess burden
Tax incidence Laffer curve · Optimal tax |
|
Collection
Revenue service · Revenue stamp
Tax assessment · Taxable income Tax lien · Tax refund · Tax shield Tax residence · Tax preparation Tax investigation · Tax resistance Tax avoidance and evasion Tax shelter · Tax haven Private tax collection · Tax farming Smuggling · Black market |
|
Distribution
|
|
By country
Tax rates around the world
Tax revenues as %GDP Albania · Australia · Britain · Canada China · France · Germany India · New Zealand United States |
A value added tax (VAT) is a form of consumption tax. It is a tax on the estimated market value added to a product or material at each stage of its manufacture or distribution, ultimately passed on to the consumer. It differs from a sales tax, which is levied only at the point of purchase.
Maurice Lauré, Joint Director of the French Tax Authority, the Direction générale des impôts, was first to introduce VAT on April 10, 1954, although German industrialist Dr. Wilhelm von Siemens proposed the concept in 1918. Initially directed at large businesses, it was extended over time to include all business sectors. In France, it is the most important source of state finance, accounting for nearly 50% of state revenues.[1]
Personal end-consumers of products and services cannot recover VAT on purchases, but businesses are able to recover VAT (input tax) on the products and services that they buy in order to produce further goods or services that will be sold to yet another business in the supply chain or directly to a final consumer. In this way, the total tax levied at each stage in the economic chain of supply is a constant fraction of the value added by a business to its products, and most of the cost of collecting the tax is borne by business, rather than by the state. VAT was invented because very high sales taxes and tariffs encourage cheating and smuggling. Critics point out that it disproportionately raises taxes on middle- and low-income homes.
Contents |
Comparison with a sales tax
Value added tax (VAT) avoids the cascade effect of sales tax by taxing only the value added at each stage of production. For this reason, throughout the world, VAT has been gaining favour over traditional sales taxes. In principle, VAT applies to all provisions of goods and services. VAT is assessed and collected on the value of goods or services that have been provided every time there is a transaction (sale/purchase). The seller charges VAT to the buyer, and the seller pays this VAT to the government. If, however, the purchaser is not an end user, but the goods or services purchased are costs to its business, the tax it has paid for such purchases can be deducted from the tax it charges to its customers. The government only receives the difference; in other words, it is paid tax on the gross margin of each transaction, by each participant in the sales chain.
In many developing countries such as India, sales tax/VAT are key revenue sources as high unemployment and low per capita income render other income sources inadequate. However, there is strong opposition to this by many sub-national governments as it leads to an overall reduction in the revenue they collect as well as a loss of some autonomy.
Sales tax is normally charged on end users (consumers). The VAT mechanism means that the end-user tax is the same as it would be with a sales tax. The main difference is the extra accounting required by those in the middle of the supply chain; this disadvantage of VAT is balanced by application of the same tax to each member of the production chain regardless of its position in it and the position of its customers, reducing the effort required to check and certify their status. When the VAT system has few, if any, exemptions such as with GST in New Zealand, payment of VAT is even simpler.
A general economic idea is that if sales taxes exceed 10%, people start engaging in widespread tax evading activity (like buying over the Internet, pretending to be a business, buying at wholesale, buying products through an employer etc.) On the other hand, total VAT rates can rise above 10% without widespread evasion because of the novel collection mechanism. However, because of its particular mechanism of collection, VAT becomes quite easily the target of specific frauds like carousel fraud, which can be very expensive in terms of loss of tax incomes for states.
Principle of VAT
The standard way to implement a VAT involves assuming a business owes some percentage on the price of the product minus all taxes previously paid on the good. If VAT rates were 10%, an orange juice maker would pay 10% of the £5 per litre price (£0.50) minus taxes previously paid by the orange farmer (maybe £0.20). In this example, the orange juice maker would have a £0.30 tax liability. Each business has a strong incentive for its suppliers to pay their taxes, allowing VAT rates to be higher with less tax evasion than a retail sales tax. Behind this simple principle are the variations in its implementations, as discussed in the next section.
Basis for VATs
By the method of collection, VAT can be accounts-based or invoice-based.[2] Under the invoice method of collection, each seller charges VAT rate on his output and passes the buyer a special invoice that indicates the amount of tax charged. Buyers who are subject to VAT on their own sales (output tax), consider the tax on the purchase invoices as input tax and can deduct the sum from their own VAT liability. The difference between output tax and input tax is paid to the government (or a refund is claimed, in the case of negative liability). Under the accounts based method, no such specific invoices are used. Instead, the tax is calculated on the value added, measured as a difference between revenues and allowable purchases. Most countries today use the invoice method, the only exception being Japan, which uses the accounts method.
By the timing of collection,[3] VAT (as well as accounting in general) can be either accrual or cash based. Cash basis accounting is a very simple form of accounting. When a payment is received for the sale of goods or services, a deposit is made, and the revenue is recorded as of the date of the receipt of funds — no matter when the sale had been made. Cheques are written when funds are available to pay bills, and the expense is recorded as of the cheque date — regardless of when the expense had been incurred. The primary focus is on the amount of cash in the bank, and the secondary focus is on making sure all bills are paid. Little effort is made to match revenues to the time period in which they are earned, or to match expenses to the time period in which they are incurred. Accrual basis accounting matches revenues to the time period in which they are earned and matches expenses to the time period in which they are incurred. While it is more complex than cash basis accounting, it provides much more information about your business. The accrual basis allows you to track receivables (amounts due from customers on credit sales) and payables (amounts due to vendors on credit purchases). The accrual basis allows you to match revenues to the expenses incurred in earning them, giving you more meaningful financial reports.
Example
Consider the manufacture and sale of any item, which in this case we will call a widget. In what follows, the term "gross margin" is used rather than "profit". Profit is only what is left after paying other costs, such as rent and personnel.
Without any tax
- A widget manufacturer spends $1.00 on raw materials and uses them to make a widget.
- The widget is sold wholesale to a widget retailer for $1.20, making a gross margin of $0.20.
- The widget retailer then sells the widget to a widget consumer for $1.50, making a gross margin of $0.30.
With a North American (Canadian provincial and U.S. state) sales tax
With a 10% sales tax:-
- The manufacturer pays $1.00 for the raw materials, certifying it is not a final consumer.
- The manufacturer charges the retailer $1.20, checking that the retailer is not a consumer, leaving the same gross margin of $0.20.
- The retailer charges the consumer $1.65 ($1.50 + ($1.50 x 10%)) and pays the government $0.15, leaving the gross margin of $0.30.
So the consumer has paid 10% ($0.15) extra, compared to the no taxation scheme, and the government has collected this amount in taxation. The retailers have not paid any tax directly (it is the consumer who has paid the tax), but the retailer has to do the paperwork in order to correctly pass on to the government the sales tax it has collected. Suppliers and manufacturers only have the administrative burden of supplying correct certifications, and checking that their customers (retailers) aren't consumers.
With a value added tax
With a 10% VAT:
- The manufacturer pays $1.10 ($1 + ($1 x 10%)) for the raw materials, and the seller of the raw materials pays the government $0.10.
- The manufacturer charges the retailer $1.32 ($1.20 + ($1.20 x 10%)) and pays the government $0.02 ($0.12 minus $0.10), leaving the same gross margin of $0.20. ($1.32 - $0.02 - $1.10 = $0.20)
- The retailer charges the consumer $1.65 ($1.50 + ($1.50 x 10%)) and pays the government $0.03 ($0.15 minus $0.12), leaving the same gross margin of $0.30 ($1.65 - $0.03 - $1.32 = $0.30).
With VAT, the consumer has paid, and the government received, the same as with sales tax. The businesses have not incurred any tax themselves. Their obligation is limited to assuming the necessary paperwork in order to pass on to the government the difference between what they collect in VAT (output tax, an 11th of their sales) and what they spend in VAT (input VAT, an 11th of their expenditure on goods and services subject to VAT). However they are freed from any obligation to request certifications from purchasers who are not end users, and of providing such certifications to their suppliers.
The advantage of the VAT system over the sales tax system is that under sales tax, the seller has no incentive to disbelieve a purchaser who says it is not a final user. That is to say the payer of the tax has no incentive to collect the tax. Under VAT, all sellers collect tax and pay it to the government. A purchaser has an incentive to deduct input VAT, but must prove it has the right to do so, which is usually achieved by holding an invoice quoting the VAT paid on the purchase, and indicating the VAT registration number of the supplier.
Limitations to example and VAT
In the above example, we assumed that the same number of widgets were made and sold both before and after the introduction of the tax. This is not true in real life.
The fundamentals of supply and demand suggest that any tax raises the cost of transaction for someone, whether it is the seller or purchaser. In raising the cost, either the demand curve shifts leftward, or the supply curve shifts upward. The two are functionally equivalent. Consequently, the quantity of a good purchased decreases, and/or the price for which it is sold increases.
This shift in supply and demand is not incorporated into the above example, for simplicity and because these effects are different for every type of good. The above example assumes the tax is non-distortionary.
A VAT, like most taxes, distorts what would have happened without it. Because the price for someone rises, the quantity of goods traded decreases. Correspondingly, some people are worse off by more than the government is made better off by tax income. That is, more is lost due to supply and demand shifts than is gained in tax. This is known as a deadweight loss. The income lost by the economy is greater than the government's income; the tax is inefficient. The entire amount of the government's income (the tax revenue) may not be a deadweight drag, if the tax revenue is used for productive spending or has positive externalities - in other words, governments may do more than simply consume the tax income. While distortions occur, consumption taxes like VAT are often considered superior because they distort incentives to invest, save and work less than most other types of taxation - in other words, a VAT discourages consumption rather than production.
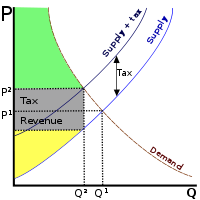
In the above diagram,
- Deadweight loss: the area of the triangle formed by the tax income box, the original supply curve, and the demand curve
- Governments tax income: the grey rectangle that says "tax revenue"
- Total consumer surplus after the shift: the green area
- Total producer surplus after the shift: the yellow area
Criticisms
The "value-added tax" has been criticized as the burden of it relies on personal end-consumers of products. Some critics consider it to be a regressive tax, meaning the poor pay more, as a percentage of their income, than the rich. Defenders argue that excising taxation through income is an arbitrary standard, and that the value-added tax is in fact a proportional tax in that people with higher income pay more at the same rate that they consume more. The effective progressiveness or regressiveness of a VAT system can also be affected when different classes of goods are taxed at different rates. To maintain the progressive nature of total taxes on individuals, countries implementing VAT have reduced income tax on lower income-earners, as well as instituted direct transfer payments to lower-income groups, resulting in lower tax burdens on the poor.[4]
Revenues from a value added tax are frequently lower than expected because they are difficult and costly to administer and collect. In many countries, however, where collection of personal income taxes and corporate profit taxes has been historically weak, VAT collection has been more successful than other types of taxes. VAT has become more important in many jurisdictions as tariff levels have fallen worldwide due to trade liberalization, as VAT has essentially replaced lost tariff revenues. Whether the costs and distortions of value added taxes are lower than the economic inefficiencies and enforcement issues (e.g. smuggling) from high import tariffs is debated, but theory suggests value added taxes are far more efficient.
Certain industries (small-scale services, for example) tend to have more VAT avoidance, particularly where cash transactions predominate, and VAT may be criticized for encouraging this. From the perspective of government, however, VAT may be preferable because it captures at least some of the value-added. For example, a carpenter may offer to provide services for cash (i.e. without a receipt, and without VAT) to a homeowner, who usually cannot claim input VAT back. The homeowner will hence bear lower costs and the carpenter may be able to avoid other taxes (profit or payroll taxes). The government, however, may still receive VAT for various other inputs (lumber, paint, gasoline, tools, etc.) sold to the carpenter, who would be unable to reclaim the VAT on these inputs (unless of course the carpenter also has at least some jobs done with receipt, and claims all purchased inputs to go to those jobs). While the total tax receipts may be lower compared to full compliance, it may not be lower than under other feasible taxation systems.
Because exports are generally zero-rated (and VAT refunded or offset against other taxes), this is often where VAT fraud occurs. In Europe, the main source of problems is called carousel fraud. Large quantities of valuable goods (often microchips or mobile phones) are transported from one member state to another. During these transactions, some companies owe VAT, others acquire a right to reclaim VAT. The first companies, called 'missing traders' go bankrupt without paying. The second group of companies can 'pump' money straight out of the national treasuries. This kind of fraud originated in the 1970s in the Benelux-countries. Today, the British treasury is a large victim.[5] There are also similar fraud possibilities inside a country. To avoid this, in some countries like Sweden, the major owner of a limited company is personally responsible for taxes. This is circumvented by having an unemployed person without assets as the formal owner.
VAT systems
European Union
The European Union Value Added Tax (EU VAT) is a value added tax encompassing member states in the European Union Value Added Tax Area. Joining in this is compulsory for member states of the European Union. As a consumption tax, the EU VAT taxes the consumption of goods and services in the EU VAT area. The EU VAT's key issue asks where the supply and consumption occurs thereby determining which member state will collect the VAT and which VAT rate will be charged.
Each Member State's national VAT legislation must comply with the provisions of EU VAT law as set out in Directive 2006/112/EC. This Directive sets out the basic framework for EU VAT, but does allow Member States some degree of flexibility in implementation of VAT legislation. For example different rates of VAT are allowed in different EU member states. However Directive 2006/112 requires Member states to have a minimum standard rate of VAT of 15% and one or two reduced rates not to be below 5%. Some Member States have a 0% VAT rate on certain supplies- these Member States would have agreed this as part of their EU Accession Treaty (for example, newspapers and certain magazines in Belgium). The current maximum rate in operation in the EU is 25%, though member states are free to set higher rates.
VAT that is charged by a business and paid by its customers is known as "output VAT" (that is, VAT on its output supplies). VAT that is paid by a business to other businesses on the supplies that it receives is known as "input VAT" (that is, VAT on its input supplies). A business is generally able to recover input VAT to the extent that the input VAT is attributable to (that is, used to make) its taxable outputs. Input VAT is recovered by setting it against the output VAT for which the business is required to account to the government, or, if there is an excess, by claiming a repayment from the government.
The VAT Directive (prior to 1 January 2007 referred to as the Sixth VAT Directive) requires certain goods and services to be exempt from VAT (for example, postal services, medical care, lending, insurance, betting), and certain other goods and services to be exempt from VAT but subject to the ability of an EU member state to opt to charge VAT on those supplies (such as land and certain financial services). Input VAT that is attributable to exempt supplies is not recoverable, although a business can increase its prices so the customer effectively bears the cost of the 'sticking' VAT (the effective rate will be lower than the headline rate and depend on the balance between previously taxed input and labour at the exempt stage).
The Nordic countries
MOMS (Danish: merværdiafgift, formerly meromsætningsafgift), Norwegian: merverdiavgift (bokmål) or meirverdiavgift (nynorsk) (abbreviated MVA), Swedish: mervärdesskatt (earlier mervärdesomsättningsskatt), Icelandic: virðisaukaskattur (abbreviated VSK) or Finnish: arvonlisävero (abbreviated ALV) are the Nordic terms for VAT. Like other countries' sales and VAT taxes, it is an indirect tax.
In Denmark, VAT is generally applied at one rate, and with few exceptions is not split into two or more rates as in other countries (e.g. Germany), where reduced rates apply to essential goods such as foodstuffs. The current standard rate of VAT in Denmark is 25%. That makes Denmark one of the countries with the highest value added tax, alongside Norway and Sweden. A number of services are not taxable, for instance public transportation of private persons, health care services, publishing newspapers, rent of premises (the lessor can, though, voluntarily register as VAT payer, except for residential premises), and travel agency operations.
In Finland, the standard rate of VAT is 23%, along with all other VAT rates, excluding the zero rate.[6] In addition, two reduced rates are in use: 12% (reduced in October 2009 from 17% for non-restaurant food, from July 2010 will encompass restaurant food also), which is applied on food and animal feed, and 8%, which is applied on passenger transportation services, cinema performances, physical exercise services, books, pharmaceuticals, entrance fees to commercial cultural and entertainment events and facilities. Supplies of some goods and services are exempt under the conditions defined in the Finnish VAT Act: hospital and medical care; social welfare services; educational, financial and insurance services; lotteries and money games; transactions concerning bank notes and coins used as legal tender; real property including building land; certain transactions carried out by blind persons and interpretation services for deaf persons. The seller of these tax-exempt services or goods is not subject to VAT and does not pay tax on sales. Such sellers therefore may not deduct VAT included in the purchase prices of his inputs.
In Iceland, VAT is split into two levels: 25.5% for most goods and services but 7% for certain goods and services. The 7% level is applied for hotel and guesthouse stays, licence fees for radio stations (namely RÚV), newspapers and magazines, books; hot water, electricity and oil for heating houses, food for human consumption (but not alcoholic beverages), access to toll roads and music.
In Norway, VAT is split into three levels: 25% is the general VAT, 14% (formerly 13%, up on January 1, 2007) for foods and restaurant take-out (food eaten in a restaurant has 25%), 8% for person transport, movie tickets, and hotel stays. Books and newspapers are free of VAT, while magazines and periodicals with a less than 80% subscription rate are taxed. Svalbard has no VAT because of a clause in the Svalbard Treaty. Cultural events are excluded from VAT.
In Sweden, VAT is split into three levels: 25% for most goods and services including restaurants bills, 12% for foods (incl. bring home from restaurants) and hotel stays (but breakfast at 25%) and 6% for printed matter, cultural services, and transport of private persons. Some services are not taxable for example education of children and adults if public utility, and health and dental care, but education is taxable at 25% in case of courses for adults at a private school. Dance events (for the guests) have 25%, concerts and stage shows have 6%, and some types of cultural events have 0%.
MOMS replaced OMS (Danish "omsætningsafgift", Swedish "omsättningsskatt") in 1967, which was a tax applied exclusively for retailers.
| Year | Tax level (Denmark) | Name |
| 1962 | 9% | OMS |
| 1967 | 10% | MOMS |
| 1968 | 12.5% | MOMS |
| 1970 | 15% | MOMS |
| 1977 | 18% | MOMS |
| 1978 | 20.25% | MOMS |
| 1980 | 22% | MOMS |
| 1992 | 25% | MOMS |
India
Of the 28 Indian states, eight did not introduce VAT. Haryana had already adopted it on 1 April 2004.
OECD (2008, 112-13) approvingly cites Chanchal Kumar Sharma (2005) to answer why it has proved so difficult to implement a federal VAT in India. The book says:
"Although the implementation of broad-base federal VAT system has been considered as the most desirable consumption tax for India since the early 1990s, such a reform would involve serious problems for the finances of regional governments. In addition, implementing VAT in India in context of current economic reforms would have paradoxical dimensions for Indian federalism. On one hand economic reforms have led to decentralization of expenditure responsibilities, which in turn demands more decentralization of revenue raising power if fiscal accountability is to be maintained. On the other hand, implementing VAT (to make India a single integrated market) would lead to revenue losses for the States and reduce their autonomy indicating greater centralization" (Sharma, 2005, as quoted in OECD, 2008, 112-13) [5]
Chanchal Kumar Sharma (2005:929) asserts: "political compulsions have led the government to propose an imperfect model of VAT" 'Indian VAT system is imperfect' to the extent it 'goes against the basic premise of VAT'. India seems to have an 'essenceless VAT' because the very reasons for which VAT receives academic support have been disregarded by the VAT-Indian Style, namely: removal of the distortions in movement of goods across states; Uniformity in tax structure. Chanchal Kumar Sharma (2005:929) clearly states, "Local or state level taxes like octroi, entry tax, lease tax, workers contract tax, entertainment tax and luxury tax are not integrated into the new regime, which goes against the basic premise of VAT, which is to have uniformity in the tax structure. The fact that no tax credit will be allowed for inter-state trade seriously undermines the basic benefit of enforcing a VAT system, namely the removal of the distortions in movement of goods across the states."
"Even the most essential prerequisite for success of VAT i.e. elimination of [Central sales tax (CST)] has been deferred. CST is levied on basis of origin and collected by the exporting state; the consumers of the importing state bear its incidence. CST creates tax barriers to integrate the Indian market and leads to cascading impact on cost of production. Further, the denial of input tax credit on inter-state sales and inter state transfers would affect free flow of goods." (Sharma,2005:922)
The greatest challenge in India, asserts Sharma (2005) is to design a sales tax system that will provide autonomy to subnational levels to fix tax rate, without compromising efficiency or creating enforcement problems.
The Andhra Pradesh experience
In the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh, the Andhra Pradesh Value Added Tax Act, 2005 came into force on 1 April 2005 and contains six schedules. Schedule I contains goods generally exempted from tax. Schedule II deals with zero rated transactions like exports. Schedule III contains goods taxable at 1%, namely jewellery made from bullion and precious stones. Goods taxable at 4% are listed under Schedule IV. The majority of foodgrains and goods of national importance, like iron and steel, are listed under this head. Schedule V deals with Standard Rate Goods, taxable at 14.5%. All goods that are not listed elsewhere in the Act fall under this head. The VI Schedule contains goods taxed at special rates, such as some liquor and petroleum products.
The Act prescribes threshold limits for VAT registration - dealers with a taxable turnover of over Rs.40.00 lacs, in a tax period of 12 months, are mandatorily registered as VAT dealers. Dealers with a taxable turnover, in a tax period of 12 months, between Rs.5.00 to 40.00 lacs are registered as Turnover Tax (TOT) dealers. While the former category of dealers are eligible for input tax credit, the latter category of dealers are not. A VAT dealer pays tax at the rate specified in the Schedules. The sales of a TOT dealer are all taxable at 1%. A VAT dealer has to file a monthly return disclosing purchases and sales. A TOT dealer has to file a quarterly return disclosing only sale turnovers. While a VAT dealer can buy goods for business from anywhere in the country, a TOT dealer is barred from buying outside the State of A.P.
The Act appears to be the most liberal VAT law in India . It has simplified the registration procedures and provides for across the board input tax credit (with a few exceptions) for business transactions. A unique feature of registration in Andhra Pradesh is the facility of voluntary VAT registration and input tax credit for start-ups.
The act not only provides for tax refunds for exporters (refund of tax paid on inputs used in the manufacture of goods exported) but also provides for refund of tax in cases where the inputs are taxed at 12.5% and outputs are taxed at 4%.
Gulf Cooperation Council
Increased growth and pressure on the GCC's governments to provide infrastructure to support growing urban centers, the Member States of the Persian Gulf Cooperation Treaty, which together make up the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), have felt the need to introduce a tax system in the region.
In particular, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) has clarified that government officials are studying the situation and considering implementation of a Value Added Tax. [7]
Mexico
Impuesto al Valor Agregado (IVA, "value-added tax" in Spanish) is a tax applied in Mexico and other countries of Latin America. In Chile it is also called Impuesto al Valor Agregado and in Peru it is called Impuesto General a las Ventas or IGV.
Prior to the IVA, a similar tax called impuesto a las ventas ("sales tax") had been applied in Mexico. In September, 1966, the first attempt to apply the IVA took place when revenue experts declared that the IVA should be a modern equivalent of the sales tax as it occurred in France. At the convention of the Inter-American Center of Revenue Administrators in April and May, 1967, the Mexican representation declared that the application of a value-added tax would not be possible in Mexico at the time. In November, 1967, other experts declared that although this is one of the most equitable indirect taxes, its application in Mexico could not take place.
In response to these statements, direct sampling of members in the private sector took place as well as field trips to the European countries this tax was applied or it was soon to be applied. In 1969, the first attempt to substitute the mercantile-revenue tax for the value-added tax took place. On December 29, 1978 the Federal government published the official application of the tax beginning on January 1, 1980 in the Official Journal of the Federation (Diario Oficial de la Federación).
As of 01/01/2010, the general 15% VAT rate will be increased to 16%. This rate is applied all over Mexico except for the Mexican region bordering the US states of California, Arizona, New Mexico and Texas, where the VAT (IVA) tax is 10% (to be raised to 11% as of 01/01/2010.) The main exemptions are for books, food, and medicines on a 0% basis. Also some services are exempt like medical doctors attention.
New Zealand
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a Value Added Tax introduced in New Zealand in 1986, which is currently 12.5%. It is notable for exempting few items from the tax. From 1 October 2010 will be increased to 15%.
Australia
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a Value Added Tax introduced in Australia in 2000, which is collected by the Federal Government but a percentage is given to the State Governments. The Australian Constitution restricts the ability of individual States to collect excises or sales taxes. Whilst the rate is currently set at 10%, there are many domestically consumed items that are effectively zero-rated (GST-free) such as fresh food, education, and health services, as well as exemptions for Government charges and fees that are themselves in the nature of taxes.
Canada
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a Value Added Tax introduced by the Federal Government in 1991 at a rate of 7%, later reduced to the current rate of 5%. A Harmonized Sales Tax (combined GST and provincial sales tax) is collected in New Brunswick , Newfoundland (13%),Nova Scotia (15%), Ontario (13%) and British Columbia (12%). Advertised prices for goods generally do not include taxes; instead, tax is calculated at the cash register. Basic groceries, prescription drugs, inward/outbound transportation and medical devices are exempt.
United States
Most states have a retail sales tax charged to the end buyer only. Unlike in the VAT, wholesale sales and sales of raw materials or unfinished goods are not taxed. A common misconception is that sales to businesses are untaxed. Sales to businesses are taxed if the business (or its workers) are the end users of a consumer good.
State sales taxes range from 0%-13% and municipalities often add an additional tax in the form of a local sales tax.[8] In most stores, the price tags and/or advertised prices do not include the taxes, and the taxes are added at the cash register before the customer pays. In some states, no sales tax is charged for services. (In many states, a use tax is imposed on items ordered online or bought in a lower or no sales tax state, and brought into the taxpayer's home state). This is a key difference between most sales taxes levied throughout the United States and the value added tax system in many other countries.
In the United States, the state of Michigan used a form of VAT known as the "Single Business Tax" (SBT) as its form of general business taxation. It is the only state in the United States to have used a VAT. When it was adopted in 1975, it replaced seven business taxes, including a corporate income tax. On August 9, 2006, the Michigan Legislature approved voter-initiated legislation to repeal the Single Business Tax, which became effective January 1, 2009.[9]
House Speaker Nancy Pelosi stated in October 2009 that a new, national VAT was "on the table" to help the federal government garner needed revenues.[10] After her speech, the Americans for Tax Reform group urged the public to contact their members of Congress to oppose this potential measure.[11] President Barack Obama was reported to be open to a national VAT.[12] One day later, US Treasury Secretary Tim Geithner stated that President Obama does not support a VAT for the US.[13]
Robert J. Samuelson has estimated that a VAT would need to be about 16 percent because, although an 8 percent would theoretically suffice, there would be huge pressures to exempt groceries, rent and housing, health care, education, and charitable groups.[14]
Tax rates
EU countries
| Country | Standard rate | Reduced rate | Abbr. | Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20% | 12% or 10% | USt. | Umsatzsteuer | |
| 21% | 12%, 6% or 0% in some cases | BTW TVA MWSt |
Belasting over de toegevoegde waarde Taxe sur la Valeur Ajoutée Mehrwertsteuer |
|
| 20% | 0% or 7% | ДДС | Данък добавена стойност | |
| 15% | 5% (8% for taxi and bus transportation) | ΦΠΑ | Φόρος Προστιθέμενης Αξίας | |
| 20% | 10% | DPH | Daň z přidané hodnoty | |
| 25%[15] | n/a | moms | Meromsætningsafgift | |
| 20% | 9% | km | käibemaks | |
| 23%[16] | 13% or 9% | ALV Moms |
Arvonlisävero Mervärdesskatt |
|
| 19.6% | 5.5% or 2.1% | TVA | Taxe sur la valeur ajoutée | |
| 19% | 7% | MwSt./USt. | Mehrwertsteuer/Umsatzsteuer | |
| 23%[17] | 11% or 5.5% (16%, 8% and 4% on islands) |
ΦΠΑ | Φόρος Προστιθέμενης Αξίας | |
| 25%[18] | 18% or 5% | ÁFA | Általános forgalmi adó | |
| 21%[19] | 13.5%, 4.8% or 0% | CBL VAT |
Cáin Bhreisluacha (Irish) Value Added Tax (English) |
|
| 20% | 10% or 4% | IVA | Imposta sul Valore Aggiunto | |
| 21% | 0% or 10% | PVN | Pievienotās vērtības nodoklis | |
| 21% | 9% or 5% | PVM | Pridėtinės vertės mokestis | |
| 15% | 12%, 9%, 6%, or 3% | TVA | Taxe sur la Valeur Ajoutée | |
| 18% | 5% | VAT | Taxxa tal-Valur Miżjud | |
| 19% | 6% or 0% | BTW | Belasting over de toegevoegde waarde | |
| 22% | 7%, 3% or 0% | PTU/VAT | Podatek od towarów i usług | |
| 21%[20] | 13% or 6% | IVA | Imposto sobre o Valor Acrescentado | |
| Madeira and Azores | 15% | 8% or 4% | IVA | Imposto sobre o Valor Acrescentado |
| 24%+[21] | 9%, 5% for first time buyers of new homes under special conditions | TVA | Taxa pe valoarea adăugată | |
| 19% | 10% | DPH | Daň z pridanej hodnoty | |
| 20% | 8.5% | DDV | Davek na dodano vrednost | |
| 18%[22] | 8% or 4%[23] | IVA | Impuesto sobre el Valor Añadido | |
| Canary Islands | 5% | 0% or 2% | IGIC | Impuesto General Indirecto Canario |
| 25% | 12% or 6% | Moms | Mervärdesskatt | |
| 17.5% (will increase to 20%, as of January 4th 2011[24]) | 5% or 0% | VAT TAW |
Value Added Tax Treth Ar Werth |
Non-EU countries
| Country | Standard rate | Reduced rate | Local name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20% | 0% | TVSH = Tatimi mbi Vlerën e Shtuar | |
| 18% | 10.5% or 0% | ƏDV = Əlavə dəyər vergisi | |
| 21% | 10.5% or 0% | IVA = Impuesto al Valor Agregado | |
| 20% | 0% | AAH = Avelac’vaç aržek’i hark ԱԱՀ = Ավելացված արժեքի հարկ |
|
| 10% | 0% | GST = Goods and Services Tax | |
| 20% | ПДВ = Падатак на дададзеную вартасьць | ||
| 15% | VAT = Value Added Tax | ||
| 17% | 0% | PDV = Porez na dodanu vrijednost | |
| 12% + 25% + 5% | 0% | *IPI - 12% = Imposto sobre produtos industrializados (Tax over industrialized products) - Federal Tax ICMS - 25% = Imposto sobre circulação e serviços (Tax over commercialization and services) - State Tax ISS - 5% = Imposto sobre serviço de qualquer natureza (Tax over any service) - City tax *IPI = Imposto sobre produtos industrializados (Tax over industrialized products) can reach 60% over imported products. |
|
| 13% | IVA = Impuesto al Valor Agregado | ||
| 5% | 4.5%2, 0% | GST = Goods and Services Tax, TPS = Taxe sur les produits et services; HST = Harmonized Sales Tax, TVH = Taxe de vente harmonisée | |
| 19% | IVA = Impuesto al Valor Agregado | ||
| 16% | IVA = Impuesto al Valor Agregado | ||
| 17% | 6% or 3% | 增值税 (pinyin:zēng zhí shuì) | |
| 23% | 10% or 0% | PDV = Porez na dodanu vrijednost | |
| 16% | 12% or 0% | ITBIS = Impuesto sobre Transferencia de Bienes Industrializados y Servicios | |
| 12% | IVA = Impuesto al Valor Agregado | ||
| 10% | VAT = Value Added Tax (الضريبة على القيمة المضافة) | ||
| 13% | IVA = Impuesto al Valor Agregado | ||
| 15% | VAT = Value Added Tax | ||
| 12.5% | 0% | VAT = Value Added Tax | |
| 18% | 0% | DGhG = Damatebuli Ghirebulebis gdasakhadi დღგ = დამატებული ღირებულების გადასახადი | |
| 12% | IVA = Impuesto al Valor Agregado | ||
| 16% | 0% | VAT = Value Added Tax | |
| 3% | VAT = Value Added Tax (مالیات بر ارزش افزوده) | ||
| 25.5% | 7%4 | VSK, VASK = Virðisaukaskattur | |
| 12.5% | 4%, 1%, or 0% | VAT = Valued Added Tax | |
| 10% | 5% | PPN = Pajak Pertambahan Nilai | |
| 16%7 | Ma'am = מס ערך מוסף | ||
| 5% | Consumption tax = 消費税 | ||
| 10% | VAT = 부가세(附加稅, Bugase) = 부가가치세(附加價値稅, Bugagachise) | ||
| 3% | 0% | GST = Goods and Services Tax | |
| 16% | GST = Goods and Sales Tax | ||
| 12% | ҚCҚ = Қосымша салық құны (Kazakh) НДС = Налог на добавленную стоимость (Russian)) VAT = Value Added Tax |
||
| 16% | TVSH = Tatimi mbi Vlerën e Shtuar | ||
| 10% | TVA = Taxe sur la valeur ajoutée | ||
| 20% | GST = Goods and Sales Tax (الضريبة على القيمة المضافة) | ||
| 20% | 8%, 5% or 0% | TVA = Taxa pe Valoarea Adăugată | |
| 18% | 5% | ДДВ = Данок на Додадена Вредност, DDV = Danok na Dodadena Vrednost | |
| 10% | GST = Goods and Services Tax (Government Tax) | ||
| 16% | 11%, 0% | IVA = Impuesto al Valor Agregado | |
| 17% | PDV = Porez na dodatu vrijednost | ||
| 15% | VAT = Value Added Tax | ||
| 12.5% | GST = Goods and Services Tax | ||
| 25% | 14% or 8% | MVA = Merverdiavgift (bokmål)or meirverdiavgift (nynorsk) (informally moms) | |
| 14.5% | VAT = Value Added Tax | ||
| 16% | 1% or 0% | GST = General Sales Tax | |
| 5% | ITBMS = Impuesto de Transferencia de Bienes Muebles y Servicios | ||
| 10% | 5% | IVA= Impuesto al Valor Agregado | |
| 19% | IGV = Impuesto General a la Ventas | ||
| 12%10 | RVAT = Reformed Value Added Tax, locally known as Karagdagang Buwis | ||
| 18% | 10% or 0% | НДС = Налог на добавленную стоимость, NDS = Nalog na dobavlennuyu stoimost’ | |
| 18% | 8% or 0% | ПДВ = Порез на додату вредност, PDV = Porez na dodatu vrednost | |
| 7% | GST = Goods and Services Tax | ||
| 14% | 0% | VAT = Valued Added Tax | |
| 12% | |||
| 7.6% (8% from 2011 to 2017) |
3.6% (hotel sector) and 2.4% (consumer goods) Temporarily changing to 3.8% and 2.5% due to AI funding from 2011 to 2017. |
MWST = Mehrwertsteuer, TVA = Taxe sur la valeur ajoutée, IVA = Imposta sul valore aggiunto, TPV = Taglia sin la Plivalur | |
| 5% | |||
| 7% | VAT = Value Added Tax, ภาษีมูลค่าเพิ่ม | ||
| 15% | |||
| 18% | 8% or 1% | KDV = Katma değer vergisi | |
| 20% | 0% | ПДВ = Податок на додану вартість, PDV = Podatok na dodanu vartist’. | |
| 22% | 10% | IVA = Impuesto al Valor Agregado | |
| 20 % | НДС = Налог на добавленную стоимость | ||
| 10% | 5% or 0% | GTGT = Giá Trị Gia Tăng | |
| 12% | 11% | IVA = Impuesto al Valor Agregado |
Note 1: HST is a combined federal/provincial VAT collected in some provinces. In the rest of Canada, the GST is a 5% federal VAT and if there is a Provincial Sales Tax (PST) it is a separate non-VAT tax.
Note 2: No real "reduced rate", but rebates generally available for new housing effectively reduce the tax to 4.5%.
Note 3: These taxes do not apply in Hong Kong and Macau, which are financially independent as special administrative regions.
Note 4: The reduced rate was 14% until 1 March 2007, when it was lowered to 7%. The reduced rate applies to heating costs, printed matter, restaurant bills, hotel stays, and most food.
Note 5: VAT is not implemented in 2 of India's 28 states.
Note 6: Except Eilat, where VAT is not raised.[26]
Note 7: The VAT in Israel is in a state of flux. It was reduced from 18% to 17% on March 2004, to 16.5% on September 2005, then to 15.5% on July 2006. It was then raised back to 16.5% in July 2009 only to be lowered to its current rate of 16% on January 1, 2010. There are plans to further change it again in the near future, but they depend on political changes in the Israeli parliament.
Note 8: The introduction of a goods and sales tax of 3% on 6 May 2008 was to replace revenue from Company Income Tax following a reduction in rates.
Note 9: In the 2005 Budget, the government announced that GST would be introduced in January 2007. Many details have not yet been confirmed but it has been stated that essential goods and small businesses would be exempted or zero rated. Rates have not yet been established as of June 2007.
Note 10: The President of the Philippines has the power to raise the tax to 12% after January 1, 2006. The tax was raised to 12% on February 1.
VAT registered
VAT registered means registered for VAT purposes, i.e. entered into an official VAT payers register of a country. Both natural persons and legal entities can be VAT registered. Countries that use VAT have established different thresholds for remuneration derived by natural persons/legal entities during a calendar year (or a different period), by exceeding which the VAT registration is compulsory. Natural persons/legal entities that are VAT registered are obliged to calculate VAT on certain goods/services that they supply and pay VAT into a particular state budget. VAT registered persons/entities are entitled to a VAT deduction under legislative regulations of a particular country. The introduction of a VAT can reduce the cash economy because businesses that wish to buy and sell with other VAT registered businesses must themselves be VAT registered.
See also
- Flat tax
- Gross receipts tax
- Income tax
- Jaffa Cake – Its non-VAT status was challenged in a UK court case to determine whether Jaffa Cake was a cake or a biscuit.
- Land value tax
- List of tax rates around the world
- Missing Trader Fraud (Carousel VAT Fraud)
- Progressive tax
- Revenue On-Line Service
- Single Tax
- Turnover tax
- VAT Identification Number
- Value-Added-Tax-free imports from the Channel Islands – low value products can be imported into the EU from the Channel Islands without paying VAT
- VAT 3
- X tax
Notes
- ↑ "Les recettes fiscales" (in french). Le budget et les comptes de l’État. Minister of the Economy, Industry and Employment (France). 30 October 2009. http://www.performance-publique.gouv.fr/le-budget-et-les-comptes-de-letat/approfondir/les-recettes/les-recettes-fiscales.html. "la TVA représente 125,4 milliards d’euros, soit 49,7 % des recettes fiscales nettes de l’État."
- ↑ Books.Google.com
- ↑ Microsoft.com
- ↑ GST in Singapore: Policy Rationale, Implementation Strategy & Technical Design, Singapore Ministry of Finance, October 2004
- ↑ Carousel fraud 'has cost UK up to £16bn', The Independent, 26 July 2007
- ↑ Vuoristo, Pekka. "Hallitus sopuun ruan veroalesta", Helsingin Sanomat, 2005-08-266. Retrieved on 2009-08-26.
- ↑ Sunil Thacker "Taxation in the Gulf: Introduction of a Value Added Tax", Michigan State Journal of International Law, Vol. 17, Issue 3, p. 721, 2008-2009. Retrieved on 2009-11-19.
- ↑ State Tax Rates, July 14, 2008
- ↑ Single Business Tax - Outline of the Michigan Tax System, Citizens Research Council of Michigan, January 24, 2007
- ↑ O'Brien, Michael. Pelosi says new tax is 'on the table'. October 6, 2009. Accessed October 9, 2009.
- ↑ Ellis, Ryan. Tell Congress That You Don’t Want a VAT Tax on Everything You Buy. October 8, 2009. Accessed October 9, 2009.
- ↑ Charles Babington. Obama suggests value-added tax may be an option. April 21, 2010. Accessed April 22, 2010.
- ↑ Jordan Fabian. Geithner: Obama 'does not support' the VAT for the U.S.. April 22, 2010.
- ↑ http://www.newsweek.com/2010/04/15/the-vat-masquerade.html
- ↑ http://www.skat.dk/getFile.aspx?ID=4262&newwindow=true
- ↑ [1]
- ↑ [2]
- ↑ BBJonline.hu
- ↑ Revenue.ie
- ↑ [3]
- ↑ [4]
- ↑ LondonStockExchange.com
- ↑ LondonStockExschange.com
- ↑ BBC News
- ↑ Ram & McRae's Investors Information Package
- ↑ VAT in Eilat, ECCB
References
- (Icelandic) "Lög nr. 50/1988 um virðisaukaskatt". 1988. http://www.rsk.is/skattalagasafn/virdisaukaskattur/log/log_0501988.htm. Retrieved 2007-09-05.
- Ahmed, Ehtisham and Nicholas Stern. 1991. The Theory and Practice of Tax Reform in Developing Countries (Cambridge University Press).
- Bird, Richard M. and P.-P. Gendron .1998. “Dual VATs and Cross-border Trade: Two Problems, One Solution?” International Tax and Public Finance, 5: 429-42.
- Bird, Richard M. and P.-P. Gendron .2000. “CVAT, VIVAT and Dual VAT; Vertical ‘Sharing’ and Interstate Trade,” International Tax and Public Finance, 7: 753-61.
- Keen, Michael and S. Smith .2000. “Viva VIVAT!” International Tax and Public Finance, 7: 741-51.
- Keen, Michael and S. Smith .1996. "The Future of Value-added Tax in the European Union," Economic Policy, 23: 375-411.
- McLure, Charles E. (1993) "The Brazilian Tax Assignment Problem: Ends, Means, and Constraints," in A Reforma Fiscal no Brasil (São Paulo: Fundaçäo Instituto de Pesquisas Econômicas).
- McLure, Charles E. 2000. “Implementing Subnational VATs on Internal Trade: The Compensating VAT (CVAT),” International Tax and Public Finance, 7: 723-40.
- Muller, Nichole. 2007. Indisches Recht mit Schwerpunkt auf gewerblichem Rechtsschutz im Rahmen eines Projektgeschäfts in Indien, IBL Review, VOL. 12, Institute of International Business and law, Germany.[6]
- Muller, Nichole. 2007. Indian law with emphasis on commercial legal insurance within the scope of a project business in India. IBL Review, VOL. 12, Institute of International Business and law, Germany.
- MOMS, Politikens Nudansk Leksikon 2002, ISBN 87-604-1578-9
- Andhra Pradesh Value Added Tax Act, 2005, Andhra Pradesh Gazette Extraordinary, 25 March 2005, retrieved on 16 March 2007.
- OECD. 2008. Consumption Tax Trends 2008: VAT/GST and Excise Rates, Trends and Administration Issues. Paris: OECD.
- Serra, J. and J. Afonso. 1999. “Fiscal Federalism Brazilian Style: Some Reflections,” Paper presented to Forum of Federations, Mont Tremblant, Canada, October 1999.
- Sharma, Chanchal Kumar 2005. Implementing VAT in India: Implications for Federal Polity. Indian Journal of Political Science, LXVI (4): 915-934. [ISSN: 00019-5510][7]
- Shome, Parthasarathi and Paul Bernd Spahn (1996) "Brazil: Fiscal Federalism and Value Added Tax Reform," Working Paper No. 11, National Institute of Public Finance and Policy, New Delhi
- Silvani, Carlos and Paulo dos Santos (1996) "Administrative Aspects of Brazil's Consumption Tax Reform," International VAT Monitor, 7: 123-32.
- Tait, Alan A. (1988) Value Added Tax: International Practice and Problems (Washington: International Monetary Fund).
External links
- VAT Related Services at the Open Directory Project
- What is VAT? - a general overview from the European Commission
- Consumption Tax Act in Japan
- VAT & sales tax information from the Indian government
- UK VAT calculator